In case of wear and tear of the joint, a congenital hip disease, inflammation or after an accident, the artificial joint replacement at the hip joint may become necessary. Worldwide, 1 million hip endoprostheses are implanted every year, 95% of them are very satisfied with the results. Ian D. Learmonth therefore described hip endoprosthetics as the surgery of the century and in 2007 published an article in the Lancet entitled: “The operation of the century: total hip replacement”.
The following surgical procedures are available in hip endoprosthetics:
- the surface replacement according to McMinn
- the short shaft prosthesis
- the total endoprosthesis
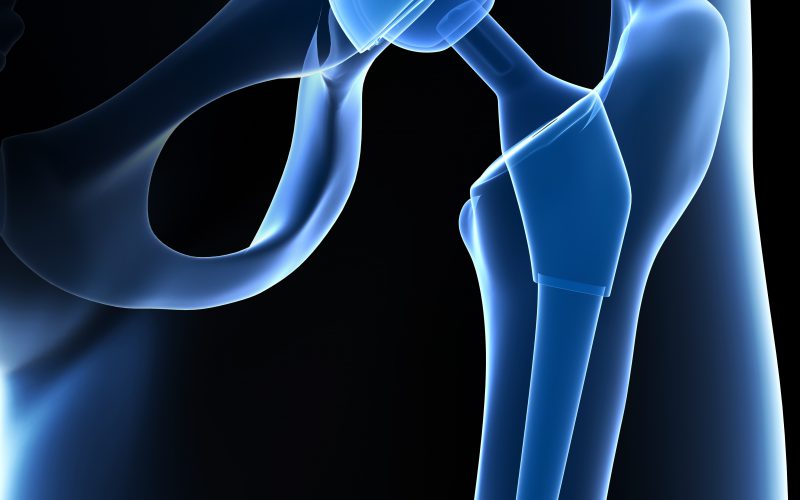
An artificial joint is used to replace the parts of the hip joint that are worn out by the disease and are responsible for the complaints: Usually these are the head of the femur and the acetabulum.
The aim of any joint replacement is to preserve as much bone substance as possible. Over the past decades, in addition to the conventional standard implants, so-called “bone-saving” hip implants have increasingly been developed, which can be a sensible alternative, especially for patients with good bone substance.
The first two surgical procedures mentioned above, especially the surface replacement as partial prosthesis and to a lesser extent the short shaft, are such “bone-saving” methods. With surface replacement, only the surface of the diseased bone is replaced. Removal of the femoral neck and femoral head, as is usual with the short stem and TEP, is not carried out here. The empirical values are highest for the TEP and lowest for the short stem.
In the standard TEP, the hip shaft is anchored in the thigh bone. A ball head sits on the shaft to replace the worn femoral head. The ball head slides in the artificial hip socket, which is anchored in the pelvis.
Which implant and which procedure ultimately makes sense depends on several factors: These include, for example, age, physique, bone quality, lifestyle habits and activities and any accompanying diseases. This can best be discussed personally during the examination in the consultation hours.